The confusion over which out-of-state companies must collect sales tax in which states was ratcheted up another level as a result of a recent U.S. Supreme Court non-decision. The Supreme Court declined to hear an appeal from New York's highest court from Amazon and Overstock, two major online merchants headquartered in another state. By so doing, it allowed the New York decision compelling certain out-of-state merchants to collect sales tax to stand. The added confusion arises from the fact that the New York decision the Supreme Court let stand was very different from one reached by Illinois' highest court just a few weeks earlier. Under similar circumstances, the Illinois court ruled Illinois could not require out-of-state merchants to collect their sales tax. Confusing enough?
It has long been established law that a state cannot require an out-of-state merchant to collect their sales tax unless that merchant has a presence in their state (“nexus” is the official term). This is based on the Constitution giving the federal government exclusive power to regulate interstate commerce. Generally, “nexus” was thought to mean some sort of physical presence – a store, warehouse, office, or something like that. Since most such retailers had a presence only in their home state, they could not be compelled to collect sales taxes for the other 49 states. That is why you rarely had to pay sales tax on something purchased via direct mail.
The states didn't much like this, but for years accepted the fact that out-of-state mail order companies could sell to their residents and not have to collect sales tax. However, the value of this lost revenue has increased tremendously over the past few years with the advent of internet sales. Today, there is much more at stake. So, the states began to look for new connections between out-of-state retailers and their states that they could claim to be sufficient “nexus” to require that retailer to collect their sales taxes. New York and Illinois both thought they found one.
Those states attempted to claim nexus based on the presence in their states of “affiliates,” persons who use their websites to send customers to the retailer's website. For example, a resident of New York might post a link on his/her website to Amazon in return for a commission on sales. The retailers do not look at these people as being a part of their business but as an independent outsider. Such a person does not create a presence by the company. The states passed legislation saying those persons are, in effect, part of the company and thereby make that company a state resident. Therefore, that out-of-state retailer, say Washington-based Amazon, must collect sales tax on sales made to residents of New York and Illinois.
In New York, the state's highest court agreed with their state's interpretation of “nexus” and demanded out-of-state retailers collect sales tax. Amazon and Overstock appealed to the U. S. Supreme Court. While the Supreme Court did not rule on the legality of New York's law, by declining to take up the case, they allowed that ruling to stand. The out-of-state merchants with in-state “affiliates” must collect their sales tax.
In Illinois, the state's highest court reached a different conclusion. While not looking at the traditional constitutional issue, the Illinois court ruled that this law violated the Internet Tax Freedom Act of 2000. That federal law prohibits discriminatory taxes on internet transactions. The Illinois court said that requiring taxes be collected because an out-of-state company was advertising on in-state people's internet sites, but not if it was advertising on in-state television stations or newspapers, was internet discriminatory. So, based on the same federal law, certain customers in Illinois aren't subject to collection of sales taxes while residents of New York are.
Obviously, this doesn't make much sense. However, the Supreme Court has shown a lack of interest in wading deeper into this issue. If balance is to be achieved, it is up to Congress to enact new laws clarifying the issue. A law has been passed by the Senate which would require all out-of-state retailers (maybe you too?) to collect sales taxes providing the merchant has over $1 million in sales annually. Currently the bill is languishing in the House of Representatives and it is questionable whether the House will act upon the bill or ignore it. The states are pressuring the House to vote yes. Many consumers and anti-tax advocates are encouraging their representatives to continue to ignore the bill. Right about now, it does not look like the House is in any great hurry to deal with an issue that many construe as amounting to a tax increase.






![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [REGNART (LE LIVRE DE)]. <i>[Le] Docteur en malice, maistre Regnard, demonstrant les ruzes et cautelles qu'il use envers les personnes…</i> Rouen, 1550. €20,000 - €30,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [REGNART (LE LIVRE DE)]. <i>[Le] Docteur en malice, maistre Regnard, demonstrant les ruzes et cautelles qu'il use envers les personnes…</i> Rouen, 1550. €20,000 - €30,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/ddd3b34c-8abc-4eae-8474-6ea05406ccd0.jpg)
![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> TRITHÈME (JEAN). <i>Polygraphie et universelle escriture cabalistique.</i> Paris, [Benoît Prévost pour] Jacques Kerver, 1561. €8,000 - €10,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> TRITHÈME (JEAN). <i>Polygraphie et universelle escriture cabalistique.</i> Paris, [Benoît Prévost pour] Jacques Kerver, 1561. €8,000 - €10,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/cbc8d1a4-d991-48c7-b788-7554a6774b0e.jpg)


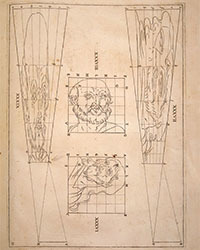
![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> VONTET (JACQUES). <i>L’Art de trancher la viande et toute sorte de fruits…</i> S.l.n.d. [probablement Lyon, vers 1647]. €20,000 - €30,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> VONTET (JACQUES). <i>L’Art de trancher la viande et toute sorte de fruits…</i> S.l.n.d. [probablement Lyon, vers 1647]. €20,000 - €30,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/21ad2e05-5544-44aa-887d-76df423e17af.jpg)

![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> HUGO (VICTOR). [Paysage spectral avec une église], [vers 1837]. €20,000 - €30,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> HUGO (VICTOR). [Paysage spectral avec une église], [vers 1837]. €20,000 - €30,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/dc734df9-0811-477f-919a-2563b8452855.jpg)
![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [HERVEY DE SAINT-DENYS (LÉON D')]. <i>Les Rêves et les Moyens de les diriger. Observations pratiques.</i> Paris, Amyot, 1867. €3,000 - €4,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [HERVEY DE SAINT-DENYS (LÉON D')]. <i>Les Rêves et les Moyens de les diriger. Observations pratiques.</i> Paris, Amyot, 1867. €3,000 - €4,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/7e769889-43a5-495e-a931-c511da576c2b.jpg)
![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> GACHET (PAUL-FERDINAND). <i>Les Chats de Gachet</i> (Manuscrit). S.d. [avant mai 1873]. €6,000 - €8,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> GACHET (PAUL-FERDINAND). <i>Les Chats de Gachet</i> (Manuscrit). S.d. [avant mai 1873]. €6,000 - €8,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/855dc2c0-17e3-4562-a1cc-2e7265c3769c.jpg)

![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [REDON (ODILON)]. PICARD (EDMOND). <i>Le Juré. Monodrame en cinq actes…</i> Bruxelles, Mme veuve Monnom, 1887. €7,000 - €9,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [REDON (ODILON)]. PICARD (EDMOND). <i>Le Juré. Monodrame en cinq actes…</i> Bruxelles, Mme veuve Monnom, 1887. €7,000 - €9,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/b325eb41-450b-4bd6-851c-4125e04dfbe7.jpg)
![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [TOULOUSE-LAUTREC (HENRI DE) ET HENRI-GABRIEL IBELS]. MONTORGUEIL (GEORGES). <i>Le Café-concert.</i> Paris, [1893]. €4,000 - €5,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [TOULOUSE-LAUTREC (HENRI DE) ET HENRI-GABRIEL IBELS]. MONTORGUEIL (GEORGES). <i>Le Café-concert.</i> Paris, [1893]. €4,000 - €5,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/6588f3a0-90f2-464c-8125-a76866eabe85.jpg)
![<b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [TERRY (EMILIO)]. <i>Projet de fontaine.</i> Dessin original au stylo et à l'encre noire. 1938. €2,000 - €3,000. <b>ALDE, Mar. 11:</b> [TERRY (EMILIO)]. <i>Projet de fontaine.</i> Dessin original au stylo et à l'encre noire. 1938. €2,000 - €3,000.](https://ae-files.s3.amazonaws.com/AdvertisementPhotos/0840c8e4-4f35-4c95-b2d3-3d5addd6fd51.jpg)