A Market Under Pressure
- by Bruce E. McKinney
Market Weakness
By Bruce McKinney
The Books, Manuscripts and Ephemera market at auction, as evidenced by both declining prices and percentage of lots sold, continues to be under extreme pressure. In the rooms, the bubble that saw median lot price rise from $410 to $485 between October 2006 and January 2008 has now dropped back to $400 with no evidence to suggest the correction is over. Not so many decades ago auctions regularly sold 90% or more of lots offered. Over the past five years auctions have struggled to complete even 80%, as the percentage of lots sold fell from 78% to 70%. This has occurred because consignors are demanding higher reserves than bidders feel is justified. Many other lots sell at the consignor's reserve [their minimum acceptable bid] with only a single bidder up against the often hidden reserve. Consequently, many lots go unsold and the overall percentage of lots sold declines. Such an approach has the perverse effect of significantly distorting market value even as sales are recorded. As well, from 1999 to 2007 the Americana Exchange, while recording well over 1.5 million auction lots, recorded a 28% increase current valuation followed by a 20% reduction in 2008. The price index today is the same as 2003. During the same period the dollar's purchasing power declined by 17%.
While it is difficult to say what an acceptable 'sell' rate is, historically it's been much higher than it is today. When this weakness is factored in the numbers look less promising.
That said, auction houses are independent, make policies, describe material, and promote sales each in unique combinations and as a result achieve unique outcomes. In the AED auction indexes that we maintain and update monthly, sell through rates are established for both individual houses and the field as a whole. In these indexes 45% of the houses have consistently achieved sell through rates of at least 80%. This suggests that high reserves are a strategy for obtaining consignments and are employed by only about half of the houses.
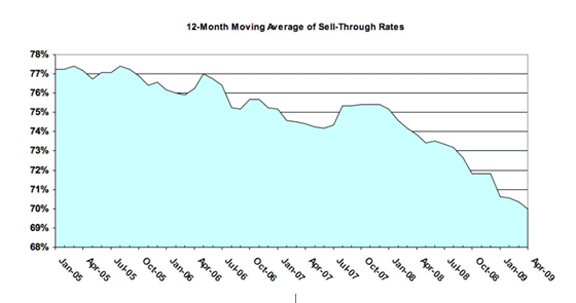
Sell though rates overall have been declining for some time as the "12 Month Sell Through Moving Average" graph shows. During the July 2007 – January 2008 period the percentage of lots sold actually rose but for the period January 2004 to April 2009 the percentage of lots sold fell from 77% to 70%. These results are subject to interpretation.
The impact of "reserves" seems to be weighing heavily on the market. We know this because if 45% of the auction houses can consistently sell 80% of their lots we can assume the other houses could also if not for minimum prices they have agreed to impose [often secretly] upon bidders. Such reserves are not uncommon but when they cause auction sell-through rates to precipitously decline they are clearly interfering with the market's ability to reprice material appropriately. Of course when prices are rising few auction houses says no. In a down market it's particularly important to let the chips fall when demand is declining. We are in such a period today and the adjustment will be more protracted if prices are held artificially high. They will in time adjust and no auction house, while catering to consignors, can afford to alienate buyers with obscured reserves that mislead them into paying above market prices.